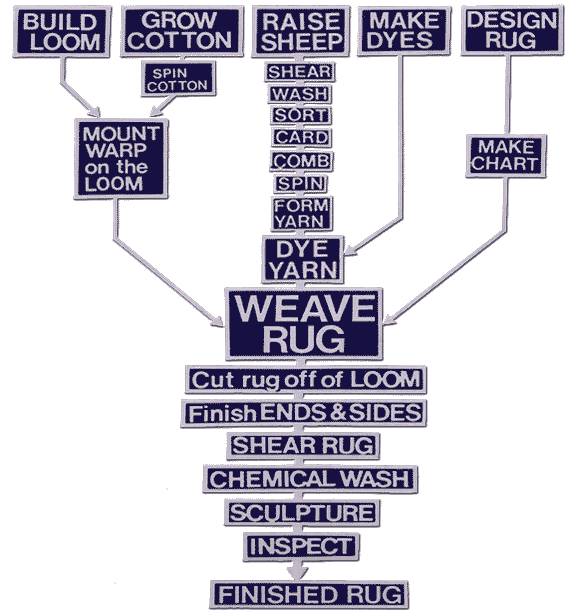
FROM SHEEP TO RUG

WOOL
FACTORS THAT DETERMINE & INSURE QUALITY:
- SPECIAL BREED -
- Out of 952 breeds of sheep - only a select few qualify to meet the quality requirements of the wool usedin the production of fine rugs.
- PROPER RAISING OF SHEEP -
- A special diet as well as optimal climate and altitude are provided as essential factors influencing the quality of the wool.
- The age of the sheep as well as the time of the year shearing occurs are additional important factors.
- SPECIAL SECTION OF FLEECE -
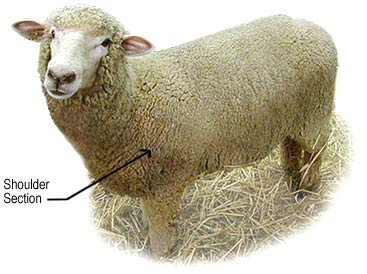
- Only the best section of the sheep's fleece is used for each rug.
- The shoulder wool is the longest and the most expensive.
- Shoulder wool gives the rug's pile excellent strength, luster, resilience, softness and durability. A fine piece of artwork deserves nothing short of the finest materials
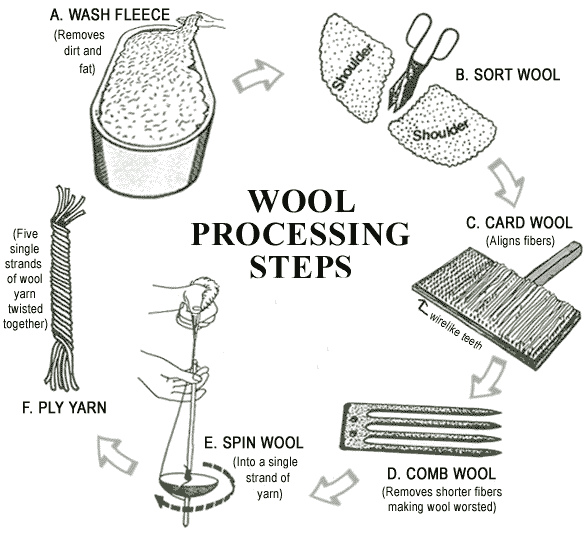
WOOL PROCESSING STEPS: WASHING, SORTING, CARDING, COMBING, SPINNING, PLYING
CHARACTERISTICS OF WOOL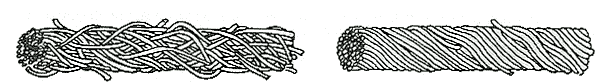
| |
| WOOLEN YARN IS SPUN AFTER CARDING |
WORSTED YARN IS NOT ONLY CARDED BUT IS GIVEN EXTRA COMBING TO REMOVE SHORTER FIBERS |
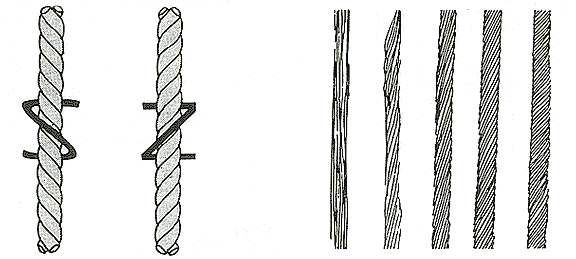 | |
| 'S' and 'Z' TWISTS SHOW DIRECTION YARN IS SPUN |
THE AMOUNT OF TWIST IN YARN DETERMINES THE STRENGTH. NO TWIST SHOWS THE FIBERS PARALLEL; THIS IS VERY SOFT WEAK YARN. WITH MORE TWIST IN THE YARN, IT BECOMES STRONGER AND HARDER. |
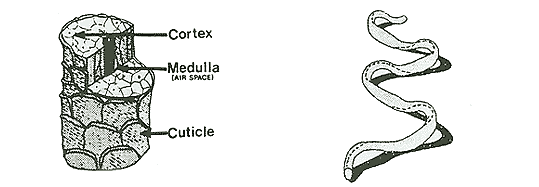 | |
| CROSS SECTION OF A WOOL FIBER THE MEDULLA IS FOUND ONLY IN COURSE WOOL. |
SINGLE WOOL FIBER SHOWING ITS NATURAL CRIMP WHICH GIVES WOOL ITS WONDERFUL RESILIENCE. |
|
COTTONAlthough wool is the best material for the rug's pile, it is not a good choice for the foundation (warp & weft). A rug made with a wool foundation will not lie flat and will be crooked (especially after washing). Only the nomadic tribes still use wool for foundations, mainly because they do not own land nor stay in one place long enough to grow cotton. Cotton makes the best foundation. Silk makes a good warp thread if extreme thinness is desired. A wool foundation can be recognized by its fringe which is darker and thicker than a cotton fringe (warp).
| |
The ADVANTAGES Of A
|
DYESFOUR TYPES OF RUG DYES | |||
| NATURAL | ANILINE | ACID | CHROME |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Today's synthetic (chrome) dyes are excellent and are not to be confused with the earlier unsatisfactory synthetic (aniline) dyes of the past.
THE RUG DESIGN PROCESS
| |
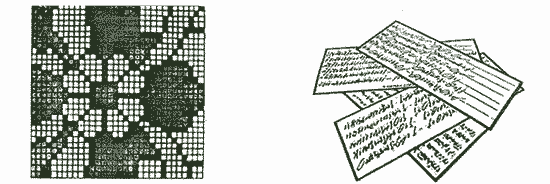
| CARTOON
A cartoon is a full scale graph paper chart which indicates to the weaver the color for each knot. Every knot is represented by a tiny square. |
TALIM In some weaving districts talim cards are used instead of a cartoon. One person reads the color and number of knots to several weavers. |
 |
HOW TO RECOGNIZE A MACHINE MADE 'ORIENTAL DESIGN' RUG
|
THE FINISH DETAILS
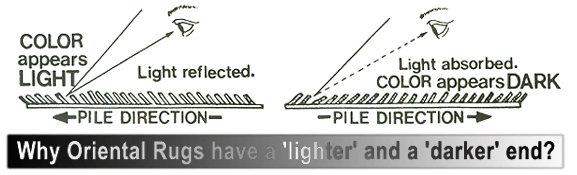
VALUE/COLOR PERCEPTION: RUG PILE DIRECTION AND LIGHT REFLECTION
The ADVANTAGES of
|
Optional Finish Tecniques:
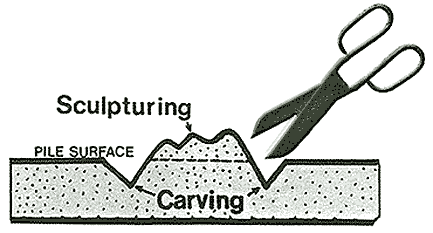
Sculpturing: Carving and incising the rug surface.
- Consumer Introduction
- Names & Places
- Rug & Knot Types
- Rug Loom Types
- Decorating Ideas
- Purchasing Guide
- Basic Rug Care
- Rug History Chart
- Glossary of Terms